So here we will discuss what is the difference between Authoritative and Non-Authoritative DNS Servers? But before we debate Authoritative vs non-Authoritative DNS we will first see what is DNS?
The Domain name system (DNS) is basically a record book of the internet. Humans are basically bad at remembering numbers (IP address) that’s the reason we just remember domain names just like google.com, facebook.com, bing.com, justgeek.in, and so on. But computers don’t understand these names they love IP addresses and each server is assigned an IP address. So DNS solves this conflict by assigning domain names with an IP address so that you can load websites on browsers and much more.
So how does DNS work?
To answer this question, we will see what happens when you type google.com in the browser.
- Your browser checks the local cache of the DNS to see if there is an IP address assigned to the domain name.
- If there is no local cache, then it will send a query to ISP and ask for the IP address of the domain.
- If ISP doesn’t have an IP address then it will send a query to root servers, and then root server will help find the IP address of the domain ( there are 13 root servers around the world ). It will redirect you to TLD servers.
- Even TLD doesn’t know the IP address of the domain, but then it will reply with the name servers of the domain.
- So the name-servers are the final authority of the domain name, they know everything about the domain like its IP address, MX Records, cname records, etc
So here is the Image which will help you to understand this better.
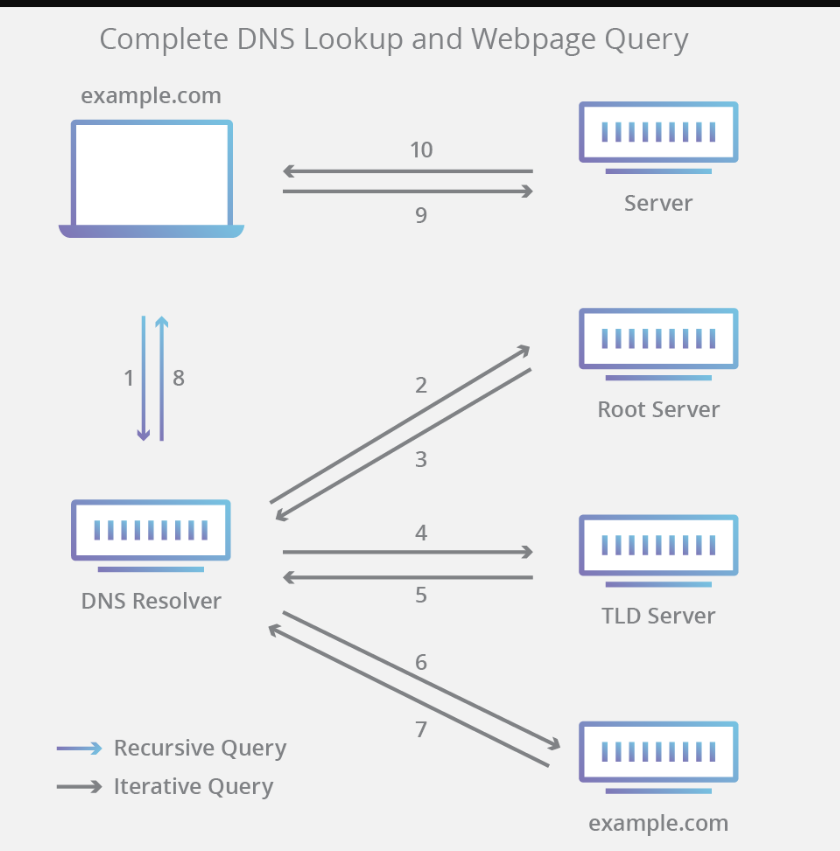
In the scenario above, everything apart from the final authority i.e name-servers are non-authoritative DNS and you may call the final authority the authoritative name-servers.
You must also see TCP or UDP, which one is better
